RECENT NEWS
28/08/2018
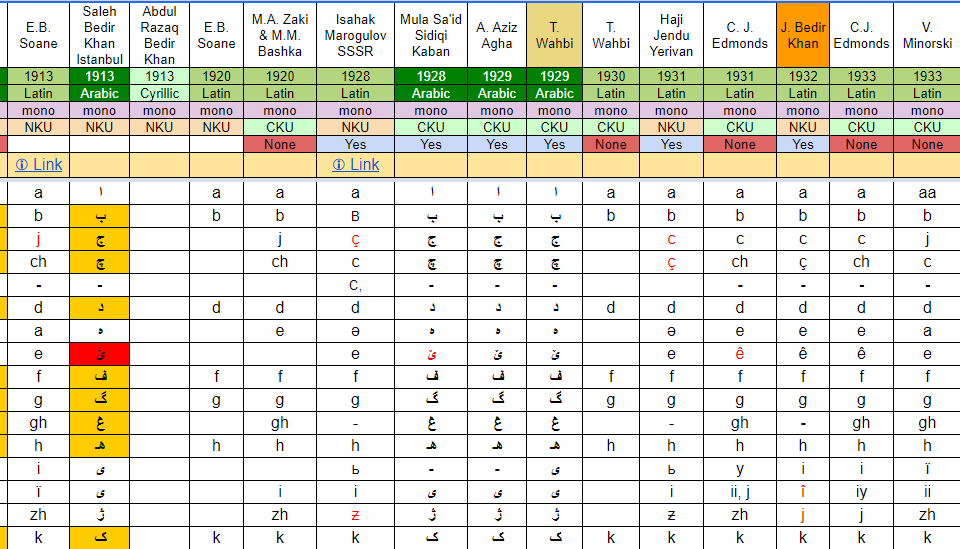
No they will not. In contrary with the framework for previous successor of Kurdish orthography by legends like J. Bedir Xan and T. Wehbí whom considered […]
28/08/2018
The Kurdish language is vibrant and multi-dialectic and has one of the richest oral literature traditions in the world. A unified writing and scripting system will […]
28/08/2018
There are several meaningful ways for individuals and organizations to get involved with projects, such as the Kurdish Academy of Languages (KAL) and KURDISTANICA. These projects […]
28/08/2018
Language is the vehicle that we commonly use to exchange ideas in our shared environment. In short, language is one of the keys that unlock the […]
28/08/2018
چرا زبان از اهمیت ویژه ای برخوردار است؟ Sat, 12/06/2010 – 15:55 — Admin زبان وسیله تبادل افکار و همچنین یکی از کلیدهای گشودن قفل ذهن […]
NEWLY POSTED
10/04/2011
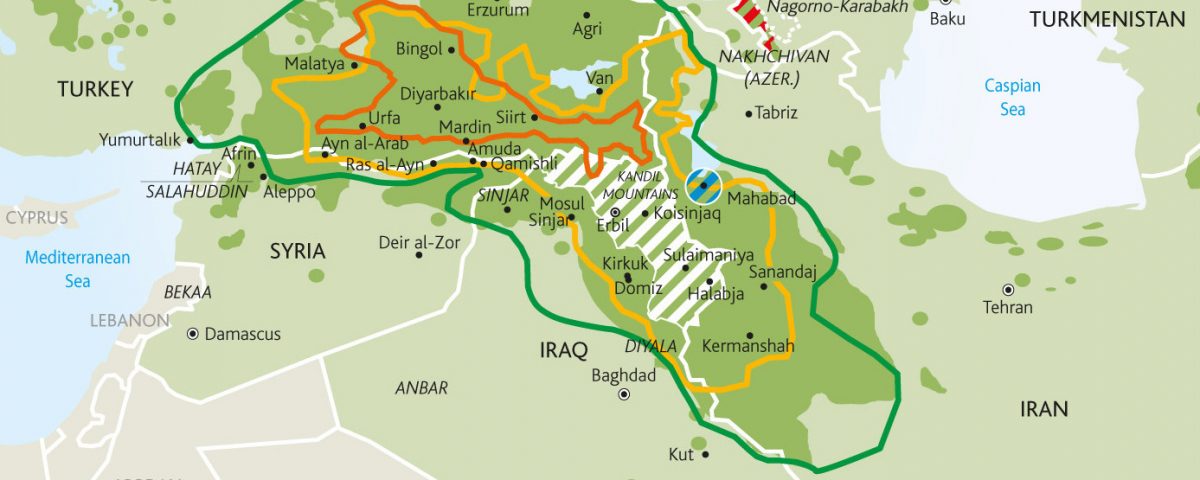
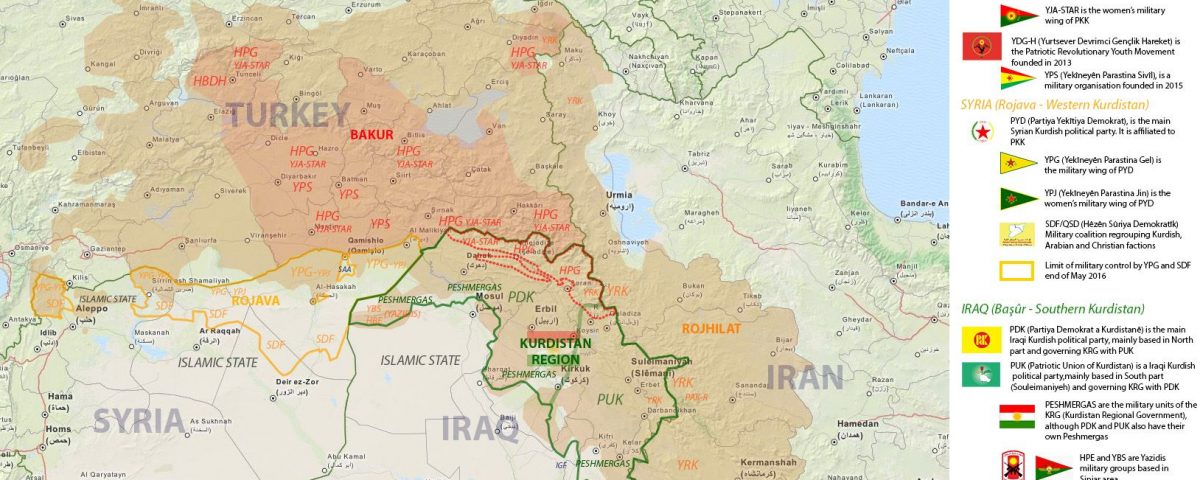
The unprejudiced academics that study Kurdish history are united in the view that the Kurds are an ancient race (1). The Kurds have lived for many […]
11/03/2011
Modern formal schooling, which is usually structured in the form of primary, secondary and higher education, relies on the extensive use of written and oral […]
06/12/2010
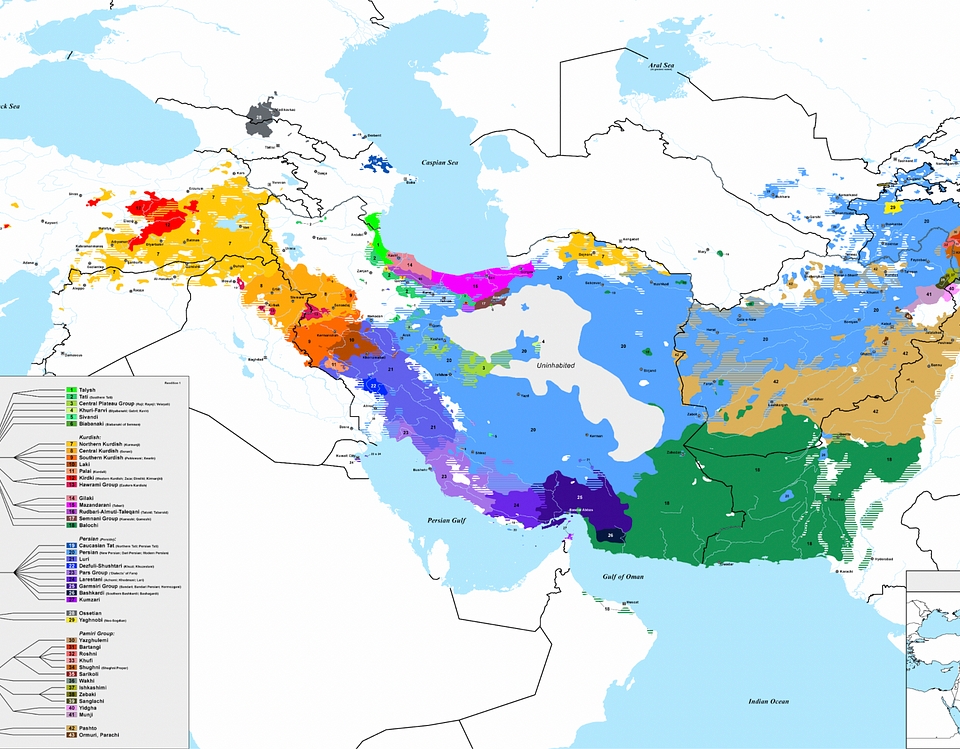
Kurdish (Kurdish: Kurdí, كوردی, Kurdî, Кöрди) language belongs to the Indo-European family of languages. Kurdish dialects are members of the northwestern subdivision of the Indo-Iranic language, […]
19/08/2010
Dr. Ali Rokhzadi (Kurdish: Elí Ruxzadí, علی روخزادی) was born in 1946 in the small village of Xalle Waze in vicinity of Xurr Xurre area of […]
25/09/2009
History of Kurdish language: Articles Section for related Articles on historical perspective of Kurdish language Ibn Khallikan’s Biographical Dictionary The Language of the Medians The origions […]
HIGHLIGHTS
Linguistic Figures
19/08/2010
Dr. Ali Rokhzadi (Kurdish: Elí Ruxzadí, علی روخزادی) was born in 1946 in the small village of Xalle Waze in vicinity of Xurr Xurre area of […]